Keep knowledgeable with free updates
Merely signal as much as the Financial coverage myFT Digest — delivered on to your inbox.
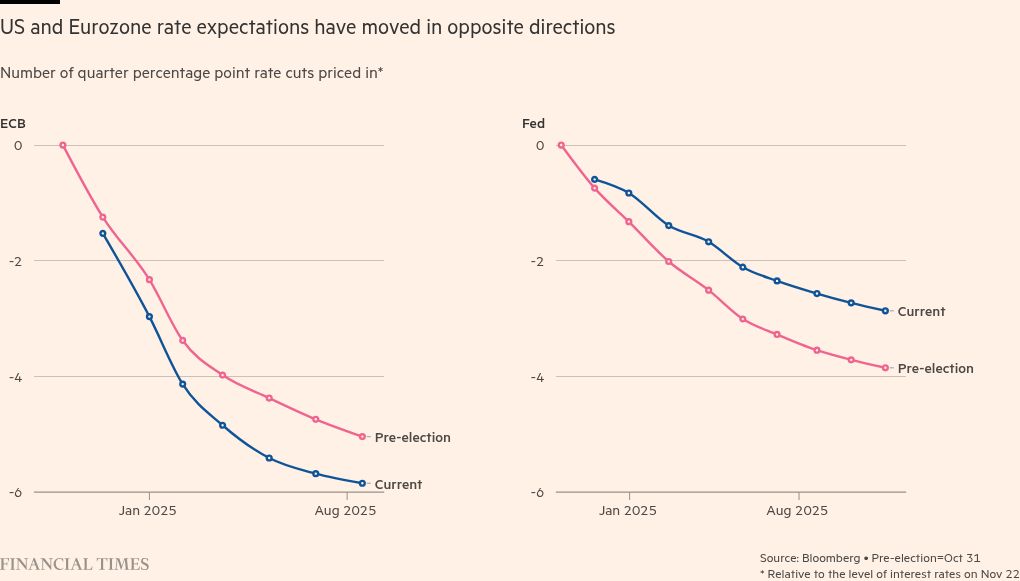
US financial coverage is on the right track to sharply diverge from Europe’s subsequent 12 months, with larger progress and inflation projections opening a transatlantic divide with the sluggish Eurozone.
The Federal Reserve is about to chop its benchmark rate of interest solely half as a lot by the tip of subsequent 12 months because the European Central Financial institution, which is going through sagging progress and inflation that undershoots its goal, in keeping with market pricing.
With Donald Trump making ready to chop taxes and enhance tariffs, US inflation is forecast to remain above 2 per cent all through the entire of 2025, in keeping with predictions compiled by Consensus Economics. Eurozone inflation is alternatively forecast to drop beneath the ECB’s goal of two per cent as quickly as February.
“We count on a divergence to open up between the loosening cycles of the Fed and the ECB as mounting inflation dangers trigger the previous to take a reasonably cautious strategy, whereas the latter responds forcefully to financial weak spot,” mentioned Jennifer McKeown, chief international economist at Capital Economics.
The parting of the methods underscores mounting considerations in regards to the embattled Eurozone financial system, the place policymakers concern additional injury from a attainable Trump-led commerce warfare. The president-elect’s coverage plans are anticipated to stoke US progress and inflation within the close to time period, with Fed chair Jay Powell stressing this month that he was in “no hurry” to decrease rates of interest.
Inflation and financial coverage moved in a broadly synchronised means throughout massive elements of the world over the previous three years as international locations skilled a generational bounce in value progress. However early strikes to ease coverage by the Fed, ECB, Financial institution of England and different western central banks this 12 months might give strategy to a extra discordant strategy in 2025.
The yield on the US two-year Treasury — which carefully tracks rate of interest expectations — rose to 4.4 per cent on the finish of the week from 3.6 per cent at the beginning of final month amid heightened considerations about inflation.

The divergence has sparked a reversal in forex markets, the place rates of interest are a driving power. The greenback, which had been weakening because the summer time, dramatically rallied towards friends by the US election as traders anticipated the influence of Trump’s tariff and tax insurance policies.
That has pushed the euro to a close to two-year low, in its greatest sell-off because the 2022 vitality disaster, with the only forex additional unsettled by weaker financial knowledge that has pushed up the possibility of a half-point charge minimize by the ECB at subsequent month’s assembly.
Samuel Tombs, economist at Pantheon Macroeconomics, mentioned the US unemployment charge was nonetheless low sufficient and inflation expectations excessive sufficient “to counsel a renewed burst of inflation . . . turns into embedded.”
He added: “It’s conceivable the Fed must finish its easing cycle prematurely if Mr Trump implements his agenda rapidly.”
Tom Barkin, president of the Richmond Fed and a voting member on this 12 months’s policy-setting Federal Open Market Committee, instructed the Monetary Occasions final week that returning charges to a extra “impartial” degree that now not crimps progress “might occur fairly slowly if you happen to thought you wanted to proceed to lean towards the inflationary breezes”.
Economists now count on US financial progress at 2.7 per cent in 2024, up from lower than 1 per cent forecast in October 2023, in keeping with Consensus Economics. For subsequent 12 months, economists revised their US financial progress forecasts to 1.9 per cent, up from 1.6 per cent anticipated in March.

The pattern is heading in the other way within the Eurozone, the place progress projections have been downgraded to 0.7 per cent this 12 months and 1.1 per cent 12 months. In the summertime, economists anticipated progress of 1.4 per cent within the bloc for 2025. Some enterprise surveys counsel that the Euro space financial system might fall into recession, mentioned McKeown at Capital Economics, “which might be a stark distinction with the resilience of the US financial system”.
Markets are pricing in additional than 1.5 share factors of charge cuts by the tip of subsequent 12 months for the ECB. This is able to take the deposit charge from the present 3.25 per cent to 2 per cent as early as June and beneath that by the tip of the 12 months. Economists polled by Consensus Economics count on a median charge of two.15 per cent by December 2025.
In distinction, within the US, markets count on a lower than 0.7 share factors minimize by the tip of subsequent 12 months from the present charge of 4.5 per cent to 4.75 per cent. Economists count on a median charge of three.375 per cent.
“The ECB’s focus is more and more shifting to financial progress considerations, and away from inflation worries,” mentioned Andrzej Szczepaniak, an economist on the funding financial institution Nomura. “In the end, we imagine the ECB will likely be pressured to chop charges to beneath impartial to help the financial system.”
Within the UK, markets count on gradual BoE charge cuts following the upward revisions to GDP progress and inflation on account of the measures introduced within the Autumn Funds.
UK financial progress has additionally been stronger than anticipated within the first half of the 12 months, whereas inflation rose greater than forecast to 2.3 per cent in October. Markets count on charges to fall to about 4 per cent by the tip of subsequent 12 months from the present charge of 4.75 per cent.
Further reporting by Olaf Storbeck in Frankfurt and Colby Smith in Washington